Axon從頭到末端又分成axon hillock、axon proper、axon terminal,分支則又分axon collaterals及recurrent collaterals。為本篇將說明是以什麼為依據,來稱呼不同小段,以及axon terminal的功能。
若想了解神經細胞(neurons)的架構;染色時常用染劑;細胞骨架(cytoskeleton)的種類及功能;如何區分axons及dendrites?MAPs (microtubule-associated proteins)是什麼;Tau與阿茲海默氏症的關係,請參考文章神經細胞neurons及細胞骨架cytoskeleton (圖片 + 重點)。
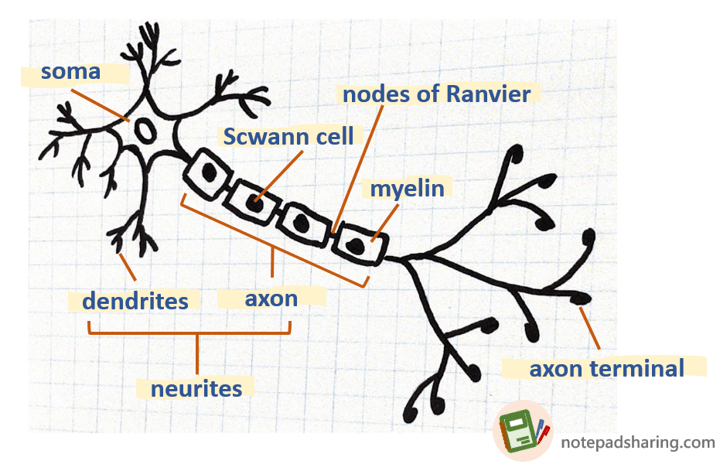
Axon
Axon的直徑從1~25 nm都有,這也導致了神經衝動(nerve impulses)的不同,愈粗的axon,nerve impulses愈快。(所以說別人神經大條其實是在說他反應很快)
Axon hillock/ proper/ terminal
從soma連接到axon的部分稱為軸丘axon hillock;中段粗細相同的部分稱axon proper;直到尾端才澎大,而末端腫腫圓圓的部分稱axon terminal。
Axon collaterals及recurrent collaterals
Axon的分支稱為axon collaterals,他們會和其它的neurons 進行communicate。如果接回去自己本身的soma或是鄰近細胞的dendrites,則可以稱作recurrent collaterals。
如何分辨axon和soma?
Axon沒有粗糙型ER (rough ER),如果有的話很少,也沒有核醣體(也就表示不會有蛋白質的合成,axon所需的蛋白質會由soma產出,再由axon傳遞。另外,Axon membrane上的蛋白質組成成分和soma membrane上的蛋白質組成成分不同)。
Axon terminal
- Microtubules不會延伸到axon terminal。
- Axon terminal含有突觸小泡(synaptic vesicles,直徑約為50 nm)。
- Axon terminal接觸soma和dendrites的位置稱為synapse。
- 在synapse這個地方,axon terminal內側的膜有高密度的蛋白質。
- Axon terminal有超多粒線體(mitochondria),因為在釋放出neuron transmitter時會需要很多energy。
- Terminal arbor:Axon terminal的branches在同一個區域。
- Boutons en passant (buttons in passing):一些axon沿著它們的長度形成突synapses,然後terminate在其他地方。



